Do states set car insurance rates by law?
Yes and no. Car insurance rates are regulated by the states, but as long as companies observe state laws, they are free to set their own rates. Here's how state regulation of insurance rates works:
- State laws ensure that a company charges the same rates to drivers who fit the same risk profile. That still allows companies to compete by setting rates for that profile that may be lower than a competitor's.
- Insurance companies are prohibited from using certain characteristics in setting their rates. Race and religion are among those factors. California, Hawaii, and Massachusetts prohibit the use of your credit information, and other states don’t allow the use of age or gender.
- States set the minimum levels of required insurance coverage. All except New Hampshire require drivers to buy insurance, and the amount of coverage required affects the cost of a basic policy.
How car insurance rates are calculated: A detailed look
There are a few steps involved in determining the rate quote a car insurance company presents to you. Here's what happens when you submit a request for a rate quote:
- You are sorted first into a group. For example, married drivers in your ZIP code over age 25.
- The insurance company calls up the pricing information for that group. This is the same for all people who fit that profile. From here, things will be personalized further.
- Information about your vehicle is considered. Your car's year, make and model, its safety ratings, claims and crash history related to that vehicle: all of these things affect the base rate.
- Your driving history is reviewed. In a rate quote, the information you provide will be used as the basis for this portion of the rate.
- Any discounts you qualify for are subtracted from the price. The information you provide will help the insurer determine which discounts to apply.
The math is done behind the scenes according to an algorithm that weighs each factor, from your ZIP code to your car's theft statistics.
If you like the quote and complete the application, a few final steps will take place. This process is called underwriting, and it's when the insurance company does a deep dive and confirms the information you provided on your application.
- The insurance company will pull your driving record. It will consider its "lookback period", which is the number of years back the company considers tickets and accidents. That's commonly three years, but may be longer.
- Your claims history will be examined. Insurance companies have shared records of claims that are considered in rating.
- Your credit history will be reviewed. In most states, insurance companies can use credit history for rating. This is a soft pull (it doesn't affect your credit) and not the same as a FICO score.
If anything is found in the underwriting process that is different from what you entered in your quote request, it could change the final rate you pay. While the order of these steps may vary, the basics remain the same: A base rate is determined and then adjusted using surcharges and discounts.
How car insurance rate calculations work: An example
Sasha is a 32-year-old single woman in Pittsburgh who works from home. She applies for a full coverage car insurance policy for her 2021 Honda CR-V.
- Sasha is grouped by her base profile: Her ZIP code, age, gender and marital status.
- Sasha's vehicle is considered: Her 2021 Honda CR-V's safety record, value and repair costs. A base rate for Sasha's profile and vehicle are set at $1,200 a year.
- Sasha's credit is checked: Her good credit history reduces her base rate to $1,050.
- Sasha's driving record is reviewed: She was in a small, at-fault accident two years ago. A surcharge for this accident increases her base rate to $1,250 a year.
- Sasha qualifies for several discounts and rate reductions: Discounts are applied for low annual mileage, automated payments, paperless billing and for the anti-theft device installed on her car. The base rate is reduced to $1,110.
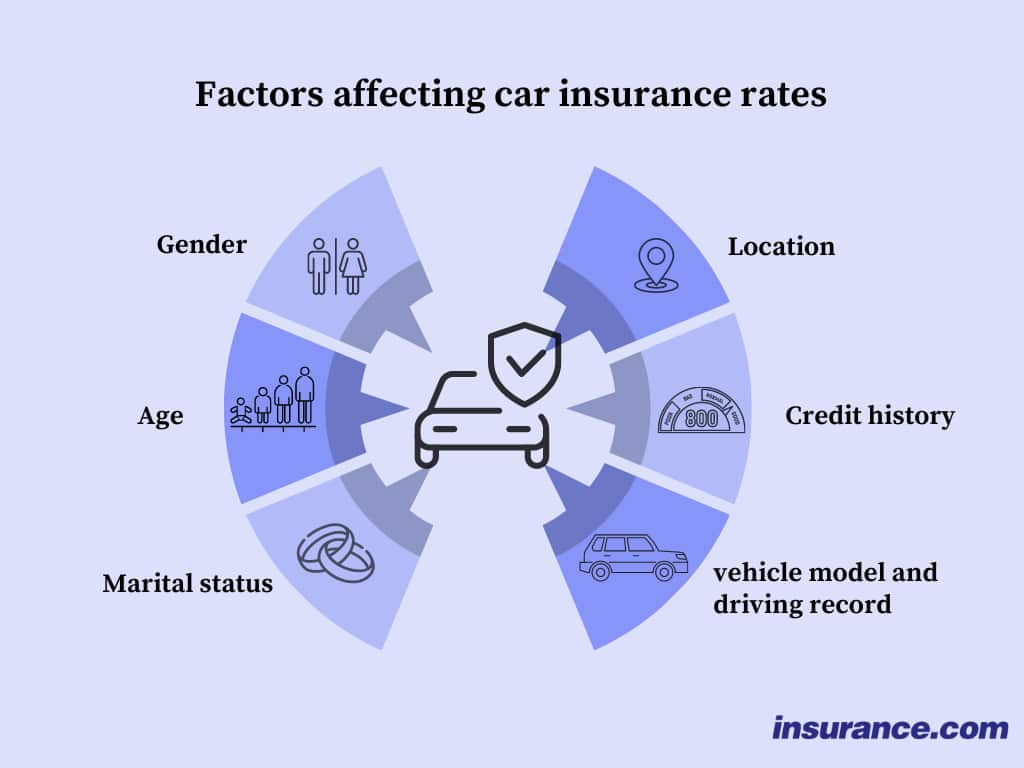
What are the factors that affect how much you pay for car insurance?
Depending on state laws, which can restrict the type of information an insurance company may use, these factors will usually affect your rates:
- Demographics. Age, gender, marital status, ZIP code, number of years you’ve been licensed, homeownership, occupation, education and even grades
- Your driving record. Accidents, traffic violations, insurance history, credit history, past claims of all types
- Your car and how you use it. Owned or financed, current value, annual mileage, claims record for all owners of that model, anti-theft devices and safety features, whether you use the car for business.
- How much coverage you buy. Liability limits, whether or not you buy comprehensive and collision (both of which carry a deductible that influences their final cost), medical payments, uninsured motorist, or extras such as rental reimbursement or towing.
Which factors affect car insurance rates the most?
While each car insurance company decides on its own how heavily to weigh a rating factor, clear patterns are evident. For most drivers, these factors tend to influence rates most:
Your ZIP code. Even if you have never filed a claimAn insurance claim is a request you make to your insurance company for coverage after your car is damaged or you have an accident. You can file a claim online, by phone, or in writing., your rate can increase dramatically simply by moving from one ZIP code to another.
Your age. Drivers with less than 10 years of experience pay more. The less experience you have, the worse the penalty. Brand-new drivers can pay an additional surchargeAn increase in your auto insurance premium due to an at-fault accident or a moving violation. Learn more about how a surcharge affects your auto insurance premiums. on top of that.
Your driving record. Claims tend to matter more than speeding tickets do. More than one of either is bad news, and so is a major violation such as a DUI.
Your credit. Insurance companies point to numerous studies that correlate poor credit scores with higher numbers of claims. The flip side: When your credit improves, your rates should decrease.
Your previous insurance coverage. If you are not currently insured, you are likely to pay much higher rates for at least your first term.
Why do insurance companies have such different rates?
Each company has many different basic rate groupings and can set different prices for those groups, basing its estimate of risk on the number and cost of claims that group has filed in the past. Then the company applies its own surcharges and discounts based on factors specific to a particular driver.
That means car insurance rates can vary considerably from one company to the next.
In high-cost states, such as Michigan, California and Louisiana, the difference can be much greater. In low-cost states such as Maine or Ohio, the differences tend to be smaller.



